Kart
(→FPGA Design) |
(→Connection) |
||
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
[[File:SummerSchool_04.jpg|thumb|Summer School '04]] | [[File:SummerSchool_04.jpg|thumb|Summer School '04]] | ||
| − | [[File:Kart.jpg|600px|Demo Kart]] | + | [[File:Kart I2C.jpg|600px|Demo Kart]] |
The work of the students can be summarized in four main tasks: | The work of the students can be summarized in four main tasks: | ||
* design and assembly of the chassis | * design and assembly of the chassis | ||
* analysis of the motor driver circuits (DC and stepper) | * analysis of the motor driver circuits (DC and stepper) | ||
| − | * | + | * configuration of the controlling FPGAs |
| − | * | + | * completion and extension of the control GUI on the smartphone |
== System Architecture == | == System Architecture == | ||
| Line 23: | Line 23: | ||
A Bluetooth receiver on the kart communicates via an [[kart/serial link|RS232 serial link]] with the FPGA control board. | A Bluetooth receiver on the kart communicates via an [[kart/serial link|RS232 serial link]] with the FPGA control board. | ||
| + | This board stores the control values in a set of [[kart/serial link#Registers|registers]] and dispatches them at a regular interval on an I2C link. | ||
| + | The master also reads data values from the slave boards, stores them into a second set of registers and sends the corresponding information at a regular pace over the RS232 with a very simple [[kart/serial link#Serial link protocol|protocol]]. | ||
| − | The control is distributed over several FPGA boards connected together via [[kart/I2C link|I2C]]: | + | The control is distributed over several FPGA boards connected together via [[kart/I2C link|I2C]]. |
| − | * | + | These base boards each hold a slave function board: |
| + | * A Bluetooth RS232 modem sits on the I2C master FPGA | ||
* A [[Kart/DC motor controller|DC motor controller]] receives a speed value and builds a PWM and a direction control. | * A [[Kart/DC motor controller|DC motor controller]] receives a speed value and builds a PWM and a direction control. | ||
* A [[Kart/stepper motor controller|stepper motor controller]] receives the desired angle and builds the coil controls signals. | * A [[Kart/stepper motor controller|stepper motor controller]] receives the desired angle and builds the coil controls signals. | ||
* A [[Kart/sensor board|sensor board]] manages I/O comprising proximity sensors, hall sensors (for the driving speed) and LEDs. | * A [[Kart/sensor board|sensor board]] manages I/O comprising proximity sensors, hall sensors (for the driving speed) and LEDs. | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
== Components == | == Components == | ||
| Line 43: | Line 41: | ||
Existing daughterboards are: | Existing daughterboards are: | ||
| − | * the [[Kart/RS232 board| serial interface board]] or the [[Kart/Bluetooth Bluetooth interface board]] | + | * the [[Kart/RS232 board| serial interface board]] or the [[Kart/Bluetooth|Bluetooth interface board]] |
* a [[Kart/DC motor controller|DC motor controller]] | * a [[Kart/DC motor controller|DC motor controller]] | ||
* a [[Kart/stepper motor controller|stepper motor controller]] | * a [[Kart/stepper motor controller|stepper motor controller]] | ||
Revision as of 13:10, 2 June 2015
|
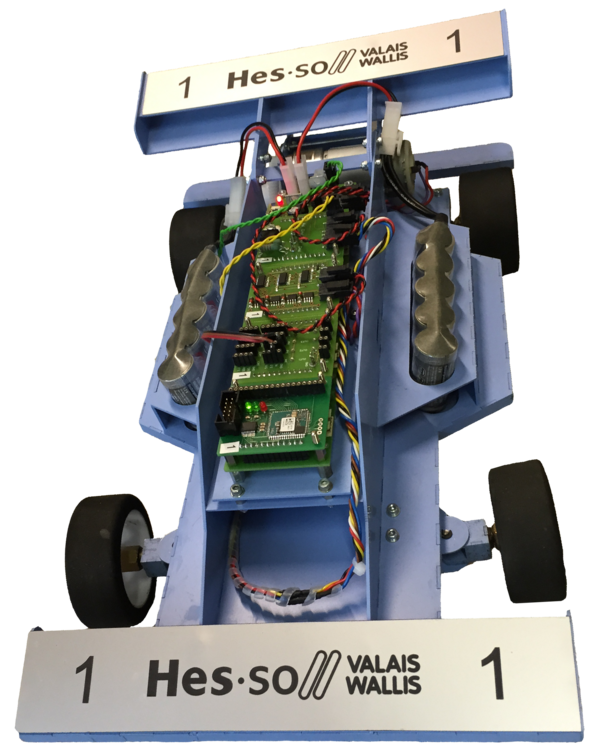
The Kart module (214_Pr1) is a Summer School module for students between 2. and 3. semester. It's a home-made car remotely controlled by a smart-phone.
The work of the students can be summarized in four main tasks:
- design and assembly of the chassis
- analysis of the motor driver circuits (DC and stepper)
- configuration of the controlling FPGAs
- completion and extension of the control GUI on the smartphone
System Architecture
The kart is controlled by a smartphone via Bluetooth.
Distributed boards
A Bluetooth receiver on the kart communicates via an RS232 serial link with the FPGA control board. This board stores the control values in a set of registers and dispatches them at a regular interval on an I2C link. The master also reads data values from the slave boards, stores them into a second set of registers and sends the corresponding information at a regular pace over the RS232 with a very simple protocol.
The control is distributed over several FPGA boards connected together via I2C. These base boards each hold a slave function board:
- A Bluetooth RS232 modem sits on the I2C master FPGA
- A DC motor controller receives a speed value and builds a PWM and a direction control.
- A stepper motor controller receives the desired angle and builds the coil controls signals.
- A sensor board manages I/O comprising proximity sensors, hall sensors (for the driving speed) and LEDs.
Components
FPGA Boards
The FPGA motherboards are equipped with an AGL125 IGLOO in a VQ100 package. They connect to daughterboards which drive different parts of the Kart. The motherboards are interconnected via an I2C link.
Existing daughterboards are:
- the serial interface board or the Bluetooth interface board
- a DC motor controller
- a stepper motor controller
- an I/O board
Sensors
The sensors connected to the I/O board are:
- 1 to 4 VCNL4000 I2C Distance/Ambience Light Sensor
- 1 to 2 SS311PT Hall Sensor
- 1 ultrasound ranger
- 1 end of turn contact switch
Additionally, the power supply board comprises an ADC which provides the battery level.
Tasks
The presentation Programming Introduction gives you an overview about the structure of the software/hardware and your tasks.
FPGA Design
You'll get the FPGAs preprogrammed with a functional solution.
In addition you'll get a HDL-Designer projects, which you have to complete or adapt.
Setup
Android App
One goal is to implement an Android application that controls and monitors the kart.
Introduction
The installable package of the (or rather a) solution can be found here: Kart.apk
Android
An introduction to Android can be found here: Android Introduction
Another sample project to learn how to create vertical seek bars: Vertical SeekBar Example
Starting point
You can download the Kart eclipse project with the basic interface here: Kart.zip
You can find the instructions how to import that archive into Eclipse in the "Programming Indtroduction" presentation...
Additional Information
- Additional informations for collaborators
- To do list
- When preparing the labs, follow the setup guide